The Crucial Significance of Indigenous Trees and the Urgency for Their Planting
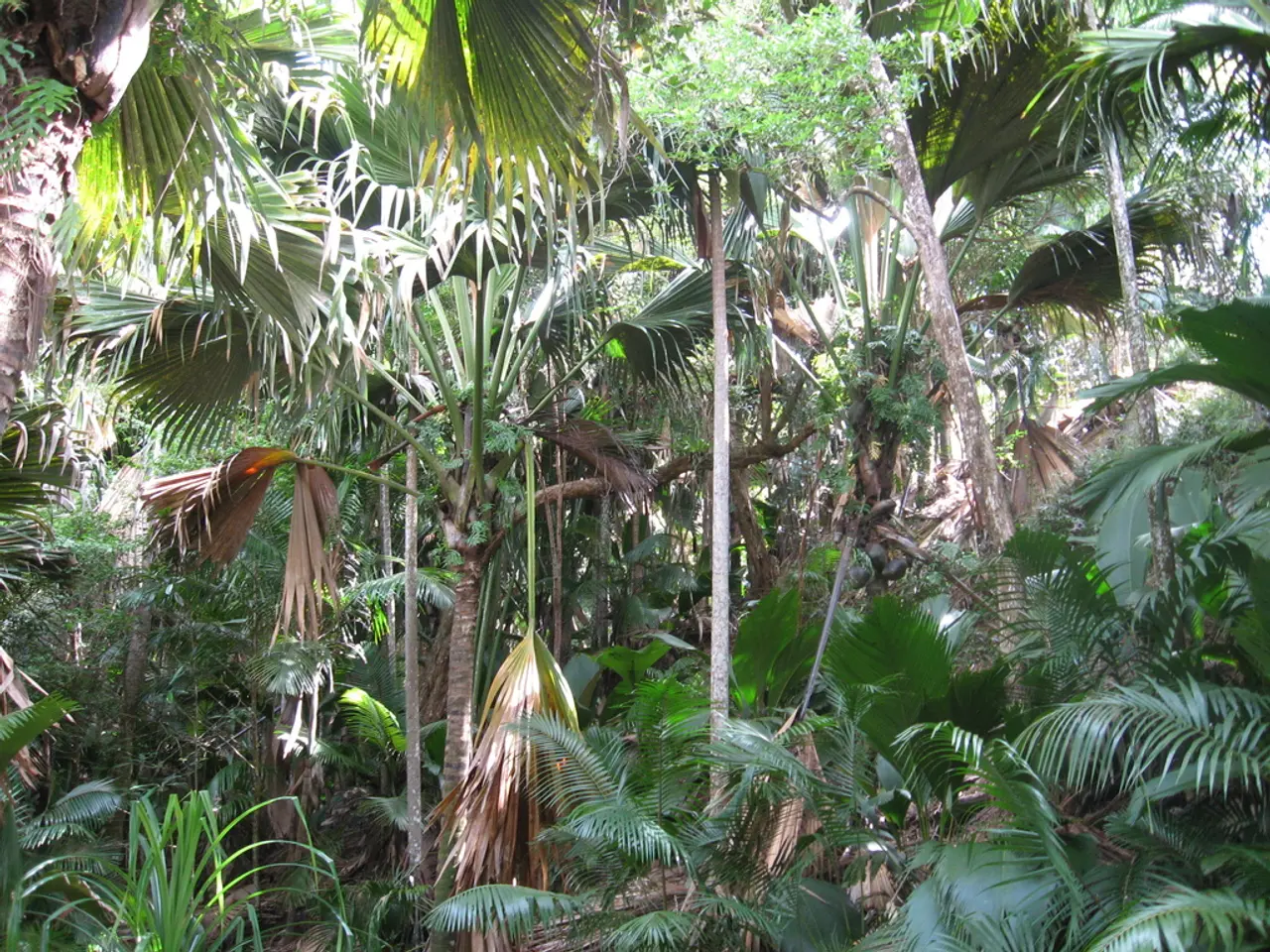
Native trees play a crucial role in our ecosystems, offering a myriad of benefits that extend beyond their aesthetic appeal. From supporting local wildlife to reducing carbon dioxide pollution, these trees are indeed a valuable asset.
Firstly, native trees are well-adapted to the local climate, precipitation level, and soil conditions, making them easy to care for. Unlike exotic trees, they do not require soil amendments or fertilizer to grow, reducing the need for artificial inputs.
This adaptation also means that native trees require less water and fewer herbicides and pesticides, making them a more sustainable choice for the environment. Moreover, they are resilient and ecologically valuable, particularly in regions where they are native, as they provide essential food and habitat for native insects and birds, supporting biodiversity.
In Germany, for instance, native trees are of significant importance. They not only offer food and habitat for native insects and birds but also contribute to the country's biodiversity. Their adaptation to local conditions makes them more resilient, providing a valuable ecological resource.
However, in regions where native trees are not naturally present, they cannot be grown due to a lack of adaptation. In such cases, exotic trees may be planted, but these trees often require fertilizer, soil amendments, and winter protection to survive in a new ecosystem.
Native trees also play a vital role in combating climate change. They can reduce carbon dioxide pollution by storing carbon dioxide in their roots, contributing to carbon sequestration. Moreover, in wild forests, regular natural fires are important for clearing brush and opening seeds. However, human habitation may make fires impossible, necessitating the planting of native trees.
In urban environments, native trees can face challenges in thriving. Nevertheless, they offer numerous benefits. For instance, they increase soil stability, reducing erosion and improving drainage. Furthermore, the insects dwelling in the overhanging vegetation of native trees are a food source for fish, benefiting various fish species in nearby bodies of water.
In conclusion, native trees are a boon for biodiversity and sustainability. They provide essential food and habitat for local wildlife, reduce carbon dioxide pollution, and support beneficial insects like bees and butterflies. While challenges may exist in urban environments, the benefits of native trees far outweigh these obstacles. Therefore, it is essential to prioritise the planting and preservation of native trees for a healthier and more sustainable future.
Read also:
- Jaguar Swimming Distance Breaks Species Record, Puzzles Researchers
- Top 10 Austin-Based Advertising Firms Worth Exploring
- Comprehensive Guide to Electric Vehicle Infotainment: Nearly all key aspects covered regarding in-vehicle entertainment systems for electric vehicles
- Simplify essential thrifty practices from yesteryears to reintroduce in 2024