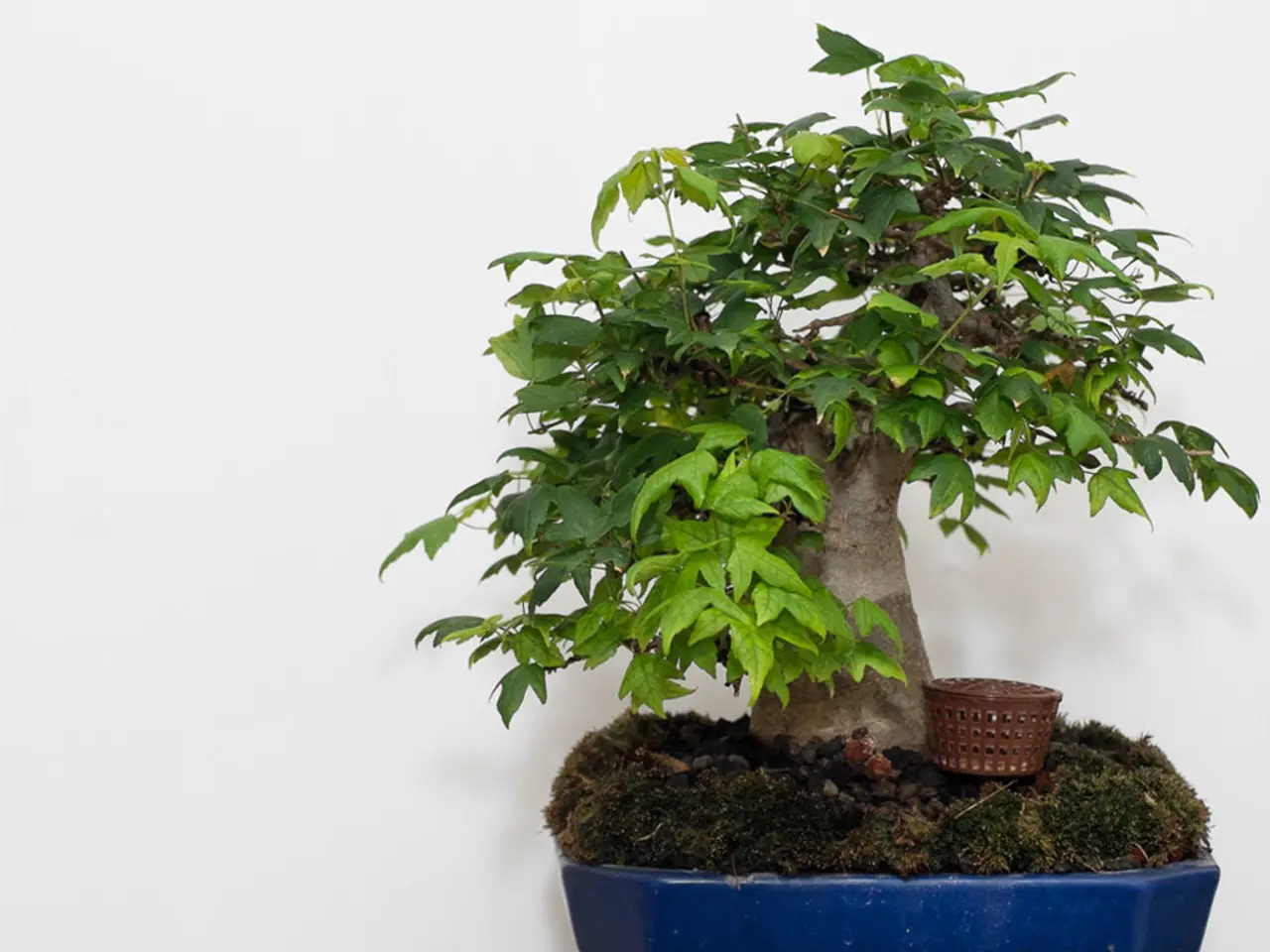
Organic and Inorganic Bonsai Nutrients: Understanding the Differences
In the world of bonsai cultivation, the choice between organic and inorganic fertilizers can have significant impacts on the health and growth of your trees. Let's delve into the benefits and drawbacks of each type to help you make an informed decision.
Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers, derived from natural sources, are generally more eco-friendly. They offer several advantages for your bonsai.
Firstly, organic fertilizers improve soil structure, promote beneficial microbial activity, and enhance soil retention of nutrients over time, contributing to the long-term health and vigor of your bonsai.
However, they do have some drawbacks. The slow release of nutrients may require more frequent applications or monitoring to ensure consistent nutrient availability. Additionally, the nutrient content in organic fertilizers can vary, making it challenging to predict the exact nutrient delivery.
Inorganic Fertilizers
Inorganic fertilizers, on the other hand, provide a quick release of nutrients, leading to rapid growth and immediate results if used correctly. They have a consistent and predictable nutrient composition, allowing for precise dosing and application.
However, inorganic fertilizers can have a higher environmental impact due to their chemical composition and potential for leaching into water systems. They also increase the risk of over-fertilization, which can cause root burn, leaf scorch, or other harmful effects on bonsai trees. Continuous use can lead to soil degradation by disrupting microbial activity and reducing soil fertility over time.
Making the Right Choice
The choice between organic and inorganic fertilizers depends on your priorities regarding environmental sustainability and the specific needs of your tree. Organic fertilizers are generally recommended for long-term health and sustainability, while inorganic fertilizers may be used for rapid growth under careful management.
Mixing organic and inorganic fertilizers can be beneficial but requires careful balancing to avoid nutrient overload or soil pH disruptions. It's also important to note that organic fertilizers tend to be pricier than inorganic counterparts due to the sourcing and processing of natural ingredients.
Other Considerations
Phosphorus facilitates energy transfer and supports root growth, while potassium regulates water balance and promotes overall plant health. The ideal ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) varies depending on the fertilizer type and the specific needs of your bonsai tree.
Indoor potted bonsai trees require fertilizers that cater to their unique needs, such as lower nitrogen levels and increased micronutrients, to thrive in low-light conditions.
Fertilization frequency depends on factors such as tree species, age, and growth stage, with a general guideline of every 1-2 weeks during the growing season and monthly during the dormant season.
A Balanced Approach
Organic fertilizers foster a thriving soil ecosystem, promoting soil structure, aeration, and water-holding capacity. Inorganic fertilizers offer a level of precision and control, providing quick and targeted nutrient delivery.
Inorganic fertilizers can be used sustainably by adopting responsible application practices, such as precise dosing and timing. Over-reliance on inorganic fertilizers can lead to a lack of resilience in bonsai trees, making them more susceptible to disease and pests.
For environmentally mindful enthusiasts, organic fertilizers are a natural fit, promoting a balanced soil ecosystem and gradual nutrient release. However, it's important to remember that even organic fertilizers can cause bonsai trees to grow too quickly, leading to weakened roots and brittle branches if not managed correctly.
Lastly, you can create your own organic bonsai fertilizer at home using readily available materials like compost, manure, and kitchen scraps. With the right knowledge and care, you can nurture your bonsai trees to grow strong and healthy for years to come.
- For those interested in health-and-wellness and lifestyle, creating one's own organic bonsai fertilizer at home, using compost, manure, and kitchen scraps, is a natural approach, promoting a balanced soil ecosystem and gradual nutrient release.
- In the realm of home-and-garden and gardening, organic fertilizers, derived from natural sources, are generally more eco-friendly, fostering a thriving soil ecosystem, promoting soil structure, aeration, and water-holding capacity.
- In the science of nutrition, phosphorus and potassium, along with nitrogen, play cruicial roles in bonsai tree growth and health. Phosphorus facilitates energy transfer and supports root growth, while potassium regulates water balance and promotes overall plant health.